 Different components of Neural SPH
Different components of Neural SPHAbstract
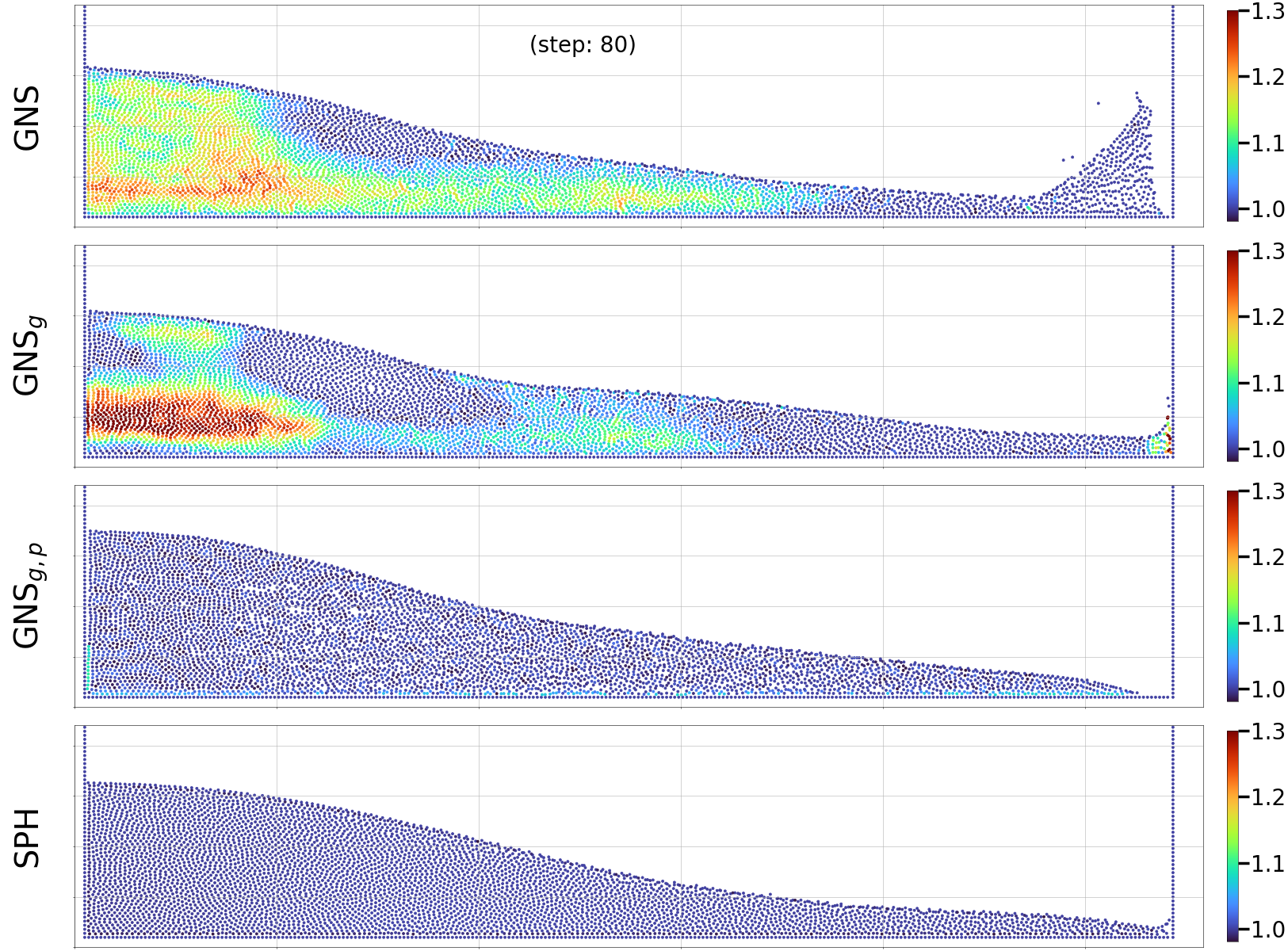
Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) is omnipresent in modern engineering and scientific disciplines. SPH is a class of Lagrangian schemes that discretize fluid dynamics via finite material points that are tracked through the evolving velocity field. Due to the particle-like nature of the simulation, graph neural networks (GNNs) have emerged as appealing and successful surrogates. However, the practical utility of such GNN-based simulators relies on their ability to faithfully model physics, providing accurate and stable predictions over long time horizons - which is a notoriously hard problem. In this work, we identify particle clustering originating from tensile instabilities as one of the primary pitfalls. Based on these insights, we enhance both training and rollout inference of state-of-the-art GNN-based simulators with varying components from standard SPH solvers, including pressure, viscous, and external force components. All neural SPH-enhanced simulators achieve better performance, often by orders of magnitude, than the baseline GNNs, allowing for significantly longer rollouts and significantly better physics modeling.